Arterial Wall Stiffness and Atherosclerosis
Jacques Ohayon, PhD
Laboratory TIMC-IMAG/DyCTiM, UJF,
CNRS UMR 5525, In3S
Faculty of Medicine of Grenoble - 38706 La Tronche Cedex, France
Email: Jacques.Ohayon@imag.fr
Is arterial wall-strain stiffening and additional process
responsible for atherosclerosis in coronary bifurcations? in vivo Study Based on Dynamic CT and MRI - Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol., 301(3):H1097-106, 2011 - Coronary bifurcations
represent specific regions of the arterial tree that are susceptible to
atherosclerotic lesions. While the effects of vessel compliance, curvature,
pulsatile blood flow and cardiac motion on coronary endothelial shear stress
have been widely explored, the effects of myocardial contraction on arterial
wall stress/strain (WS/S) and vessel stiffness distributions remain unclear. Local increase of vessel
stiffness resulting from wall-strain stiffening phenomenon – a local process due to the
nonlinear mechanical properties of the arterial wall – may be critical in the development
of atherosclerotic lesions. Therefore, the aim of this study was to quantify WS/S and
stiffness in the coronary bifurcations and to investigate correlations with
plaque sites. Anatomic coronary geometry and cardiac motion were generated based
on both computer tomography and magnetic resonance imaging examinations of
eight patients with minimal coronary disease. Computational structural analyses
using finite element method were subsequently performed and spatial luminal
arterial wall stretch (LWstretch) and stiffness (LWstiff)
distributions in the left main coronary bifurcations were calculated. Our
results show that all plaque sites were concomitantly subject to high LWStretch
and high LWStiff, with mean amplitudes 34.7 1.6% and 442.4
1.6% and 442.4 113.0
kPa, respectively. The mean LWStiff amplitude was found slightly
greater at the plaque sites on the left main coronary (mean value, 482.2
113.0
kPa, respectively. The mean LWStiff amplitude was found slightly
greater at the plaque sites on the left main coronary (mean value, 482.2 88.1 kPa)
as compared to those computed on the left anterior descending and left
circumflex coronaries (416.3
88.1 kPa)
as compared to those computed on the left anterior descending and left
circumflex coronaries (416.3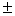 61.5 kPa and 428.7
61.5 kPa and 428.7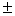 181.8
kPa, respectively). These finding suggests that local wall stiffness plays a
role in the initiation of atherosclerotic lesions.
181.8
kPa, respectively). These finding suggests that local wall stiffness plays a
role in the initiation of atherosclerotic lesions.
|
|
|
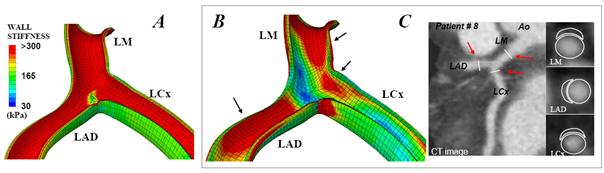
Fig. 1: Influence of cardiac contraction on the spatial distribution of the arterial wall stiffness (unit: kPa). Results show spatial wall stiffness distribution when neglecting (A) and considering (B) heart motion. All these computations were performed on patient # 8. C) CT views highlighting lesion sites and showing the cross-section for plaques located in LM, LAD and LCx branches. Arrows indicate lesion sites. |
Selected Publications
• Ohayon J, Mesnier N, Broisat A, Toczek J, Riou L, Tracqui P. Elucidating atherosclertic vulnerable plaque rupture by modeling cross substitution of ApoE-/- mouse and human plaque component stiffnesses. Biomechanics and Modeling in Mechanobiology. (in press), 2011.
• Ohayon J, Gharib AM, Garcia A, Heroux J, Yazdani SK, Malvè M, Tracqui P, Martinez MA, Doblare M, Finet G, Pettigrew RI. Is arterial wall-strain stiffening and additional process responsible for atherosclerosis in coronary bifurcations? in vivo Study Based on Dynamic CT and MRI. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 301(3):H1097-106, 2011.
• Broisat A, Toczek J, Mesnier N, Tracqui P, Ghezzi C, Ohayon J, Riou L. Assessing the low levels of mechanical stress in aortic atherosclerosis lesions from ApoE-/-mouse . Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 31(5):1007-10, 2011.
• Tracqui P, Broisat A, Toczek J, Mesnier N, Ohayon J, Riou L. Mapping elasticity moduli of atherosclerotic plaque in situ via atomic force microscopy . Journal of structural Biology 174(1):115-23, 2011.
• Heroux J, Gharib AM, Danthi NS, Cecchini S, Ohayon J, Pettigrew RI. High Affinity avb3 Integrin Targeted Optical Probe as a New Imaging Biomarker for Early Atherosclerosis: Initial Studies in Watanabe Rabbits. Mol Imaging Biol., 12(1):2-8, 2010.
• Soloperto G, Keenan NG, Sheppard MN, Ohayon J, Wood N, Pennell DJ, Mohiaddin RH, Xu XY. A combined imaging, computational and histological analysis of a ruptured carotid plaque. Artery Research, 4(2):59-65, 2010.
• Le Floc'h S, Cloutier G, Finet G, Tracqui P, Pettigrew RI, Ohayon J. On the potential of a new IVUS elasticity modulus imaging approach for detecting vulnerable atherosclerotic coronary plaques: in vitro vessel phantom study. Phys. Med. Biol., 55:5701-5721, 2010.
• Finet G., Huo Y, Riouffol G, Ohayon J, Guerin P, Kassab GS. Structure-function relation in the coronary artery tree: from fluid dynamics to arterial bifurcations. EuroIntervention, 6:J10-J15, 2010.
• Le Floc'h S, Ohayon J, Tracqui P, Finet G, Gharib AM, Maurice R, Cloutier G, Pettigrew RI. Vulnerable Atherosclerotic Plaque Elasticity Reconstruction Based on a Segmentation-Driven Optimization Procedure Using Strain Measurements: Theoretical Framework. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 28(7):1126-37, 2009.
• Kotys MS, Herzka DA, Vonken EJ, Ohayon J, Heroux J, Gharib AM, Stuber M, Pettigrew RI. Profile order and time-dependent artifacts in contrast-enhanced coronary MR angiography at 3T: origin and prevention. Magn Reson Med., 62(2):292-9, 2009.
• Eskandari H, Salcudean SE, Rohling R, Ohayon J. Viscoelastic characterization of soft tissue from dynamic finite element models. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 53(22):6569-90, 2008.
• Ohayon J, Finet G, Gharib AM, Herzka DA, Tracqui P, Heroux J, Rioufol G, Kotys MS, Elagha A, Pettigrew RI. Necrotic core thickness asnd positive arterial remodeling index: emergent biomechanical factors for evaluating the risk of plaque rupture. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol., 295(2):H717-27, 2008.
• Ohayon J, Dubreuil O, Tracqui P, Le Floc'h S, Rioufol G, Chalabreysse L, Thivolet F, Pettigrew RI, Finet G. Influence of residual stress/strain on the biomechanical stability of vulnerable coronary plaques: potential impact for evaluating the risk of plaque rupture. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol., 293(3):H1987-96, 2007.
• Boudou T., Ohayon J., Arntz Y., Finet G., Picart C., Tracqui P. An extended modeling of the micropipette aspiration experiment for the characterization of the Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio of adherent thin biological samples: Numerical and experimental studies. Journal of Biomechanics, 39:1677-85, 2006.
• Boudou T., Ohayon J., Picart C., Tracqui P. Characterization of the Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio of polyacrylamide gels using micropipette aspiration technique. Biorheology, 43(6): 721-8, 2006.